Nation On The Path Of Rapid Digitisation
CK Khanal
There has been tremendous progress in digitisation of the economy in the last few years by using modern information and communication technologies (ITC). The rapid expansion of broadband internet service in recent years, is facilitating the process of disitising the economy in almost all sectors promoting production, productivity, and transparency in the respective sectors.
According to the MIS report of Nepal Telecommunication Authority (NTA), penetration of broadband internet service has reached 81.49 per cent of the total population by mid-December 2020. The internet penetration was only 63.17 per cent by mid-December 2017.
Such progress in the expansion of broadband internet service had been possible due to the policy of the government to build Digital Nepal, said Anil Kumar Dutta, joint secretary at the Ministry of Communication and Information Technology.
The Department of Information Technology, NTA, Office of Controller of Certification, and National Information Technology Centre under the ministry are jointly working towards the digitisation of the country, Dutta said. There has been remarkable progress in the expansion of ICT services, enactment of supporting laws and policies in recent time, he added.
The government has introduced ‘Digital Nepal Framework 2076’ aiming to modernise and transform service delivery and increase production and productivity through the use of ICT. The framework has selected eight areas and 80 mid-term and long-term initiatives for the digital transformation of the country.
Under this policy framework, the government is promoting fast expansion of 4G service and other wired and wireless broadband internet service in both urban and rural areas.
Min Prasad Aryal, spokesperson at NTA, said that there has been significant improvement in the quantity and quality of internet services in recent years. Coverage of the 4G service has now reached all 77 districts of the country and more than 5 million people are using the service, he said.
According to the latest MIS report of NTA, subscribers of mobile broadband service (3G, 4G, and EVDO) have increased to 6.62 million across the country by mid-December 2020. The subscription of 4G/LTE service, which was first launched in the country on January 1st, 2017, has reached 60 per cent of the country’s total population. Subscribers of the 3G service have exceeded 11.1 million.
Besides, telecommunication service providers and internet service providers (ISPs) are aggressively expanding fixed broadband (wired and wireless) in recent times as per the policy of the government to build digital Nepal.
Aryal said that there had been significant improvement in the quality of data and voice service of telecommunication service providers under the regulatory framework of the NTA.
Moreover, the expansion of broadband internet service in remote areas under different projects utilising the Rural Telecommunication Development Fund (RTDF) has made a remarkable contribution to enhancing the access of people in broadband service.
A total of 18 packages have been launched to expand broadband internet service in rural areas under the RTDF. Under those packages, the NTA is expanding free internet service in 15,982 sites 0f 74 districts which include 702 offices of local authorities, 5,933 ward offices, 5,225 secondary schools, and 4,122 health institutions.
Of the total targeted sites, internet service has already been connected in 11,794 (73.80 per cent) sites, said Surendra Lal Hada, director of Project Division of NTA.
The NTA is providing free equipment and internet service for two years under these packages on all sites, Hada said. This project has made a tremendous contribution in digitising services of local bodies, schools, and health institutions at the same time enhancing access of people to the internet service, he said.
He, however, said that the sustainability of the internet service in those sites might be challenging after two years as it had seen in the case of free internet service provided in districts affected by 2015 earthquake. The government should bring support programme for the sustainability of the internet service.
Information Super Highway Project
The NTA is implementing Information Highway Project to lay down optical fibers along Mid Hill Highway and connecting district headquarters by utilising the RTDF.
Under this project, the government targets to lay optical fibers in 6,235 kilometers under three packages- package –I in Province 1, Province 2 and Bagmati Province, package-II in Gandaki and Lumbini Province, and package-II in Karnali and Sudurpaschim Province. Of which, optical fiber has been laid in 678 kilometers so far under package-I.
The bidding process is under progress in package-III currently whereas problem has surfaced in the works under package-II. The NTA has canceled the agreement with the contracting company due to its inability to implement the project of package-II and the Supreme Court has issued a stay order not to implement the decision.
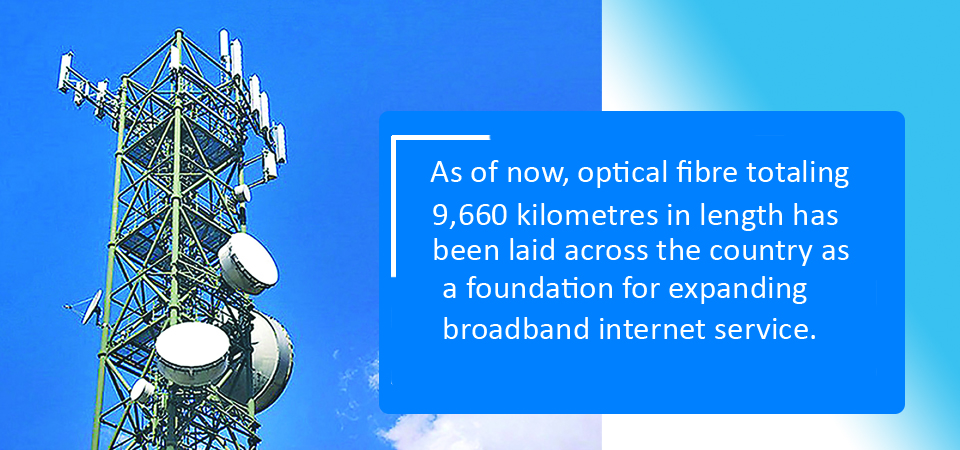
As of now, optical fibre totaling 9,660 kilometres in length has been laid across the country as a foundation for expanding broadband internet service.
Besides, the government has developed infrastructure to import internet bandwidth from two border points Kerung and Tatopani with China, removing its sole dependency on India.
From the utilisation of ICT services, there has been rapid progress in digitisation of the economy in almost all sectors of the economy ranging from trade, industry, agriculture, health to education. The lockdown imposed by the government to control the COVID-19 pandemic also played a role to speed up the pace of digitisation in the economy.
The country is gradually moving towards cashless transactions and most of the services of the government and the private sector companies are being made available online. Government authorities are using ICT in their functioning intensively in recent times enhancing productivity and transparency.
Some of the major developments towards deigitisation of the economy using ICT services include:
Online service initiated in government agencies including, customs & land revenue offices
Launching of Nagarik App to provide government service in an integrated way
Introduction of National one door system in customs
Distribution of National Identity Cards
Implementation of digital signature
Promotion of digital payment system through digital wallets, bank apps, connect IPS and QR code
Smart driving license
Web-based centralised E-attendance System in 587 agencies
Integrated office management system in government authorities.
Operation of digital forensic lab
(Khanal is a TRN journalist.)
Recent News

Do not make expressions casting dout on election: EC
14 Apr, 2022
CM Bhatta says may New Year 2079 BS inspire positive thinking
14 Apr, 2022
Three new cases, 44 recoveries in 24 hours
14 Apr, 2022
689 climbers of 84 teams so far acquire permits for climbing various peaks this spring season
14 Apr, 2022
How the rising cost of living crisis is impacting Nepal
14 Apr, 2022
US military confirms an interstellar meteor collided with Earth
14 Apr, 2022
Valneva Covid vaccine approved for use in UK
14 Apr, 2022
Chair Prachanda highlights need of unity among Maoist, Communist forces
14 Apr, 2022
Ranbir Kapoor and Alia Bhatt: Bollywood toasts star couple on wedding
14 Apr, 2022
President Bhandari confers decorations (Photo Feature)
14 Apr, 2022