Why Time Flows Back During Gamma-Ray Bursts
Djurić Vladan
The scientific publication Astrophysical Journal has published material that explains the abnormal movement of time during gamma-ray bursts. For observers, this process looks like time is running back. The appearance of gamma-ray bursts is associated with the life cycle of large star clusters. The gamma-ray burst, according to recent data, occurs before the death of a celestial body.
Black holes
The end of a star’s life is associated with overheating of the nucleus, causing black holes and neutron stars. The force of attraction increases several times, as a result of which the particles are combined into one body. Scientists say the phenomenon is like a disk. Part of the disk of a dead star is absorbed by a black hole. The rest is ejected at the speed of light throughout outer space. As a result, the celestial body becomes dark, and energy spills out in an immeasurable amount.
Just a year ago, scientists found a new case of gamma-ray burst. Depending on the sensitivity of the spectrometer, the structure of celestial bodies was different. As a result, scientists came to the conclusion that during the surge, time moves backward. To test the hypothesis, scientists used streams of red-hot plasma, accelerating a black hole. Thus, scientists tested the interaction of other objects with a black hole.
During the study, scientists found that the phenomenon has a completely normal explanation, amenable to the laws of physics. As it turned out, the spilled energy moves at different speeds depending on the matter through which the energy passes. According to the published material of the Astrophysical Journal, a black hole strongly accelerates matter, that the body begins to move through dense layers of plasma. In this case, the movement occurs much faster than with the movement of light in a similar medium.
Light particles
Based on the theory of Sergei Vavilov, dense matter slows down the movement of celestial objects, resulting in the formation of particles of light. In this case, matter will move faster than light elements. Thus, observers may get the impression that time is going back.
After the plasma slows down as much as possible, there will be a quick jump in time forward. Such a phenomenon is called relativistic image doubling, since the observer will initially see two moving matter. Soon, astrophysicists were able to recreate a simulation model of a gamma-ray burst to further study the phenomenon. The authors of the published material believe that calculations can help in researching the role of celestial elements in studying the structure of planets and the appearance of life on them.
--Pravda.ru
Recent News

Do not make expressions casting dout on election: EC
14 Apr, 2022
CM Bhatta says may New Year 2079 BS inspire positive thinking
14 Apr, 2022
Three new cases, 44 recoveries in 24 hours
14 Apr, 2022
689 climbers of 84 teams so far acquire permits for climbing various peaks this spring season
14 Apr, 2022
How the rising cost of living crisis is impacting Nepal
14 Apr, 2022
US military confirms an interstellar meteor collided with Earth
14 Apr, 2022
Valneva Covid vaccine approved for use in UK
14 Apr, 2022
Chair Prachanda highlights need of unity among Maoist, Communist forces
14 Apr, 2022
Ranbir Kapoor and Alia Bhatt: Bollywood toasts star couple on wedding
14 Apr, 2022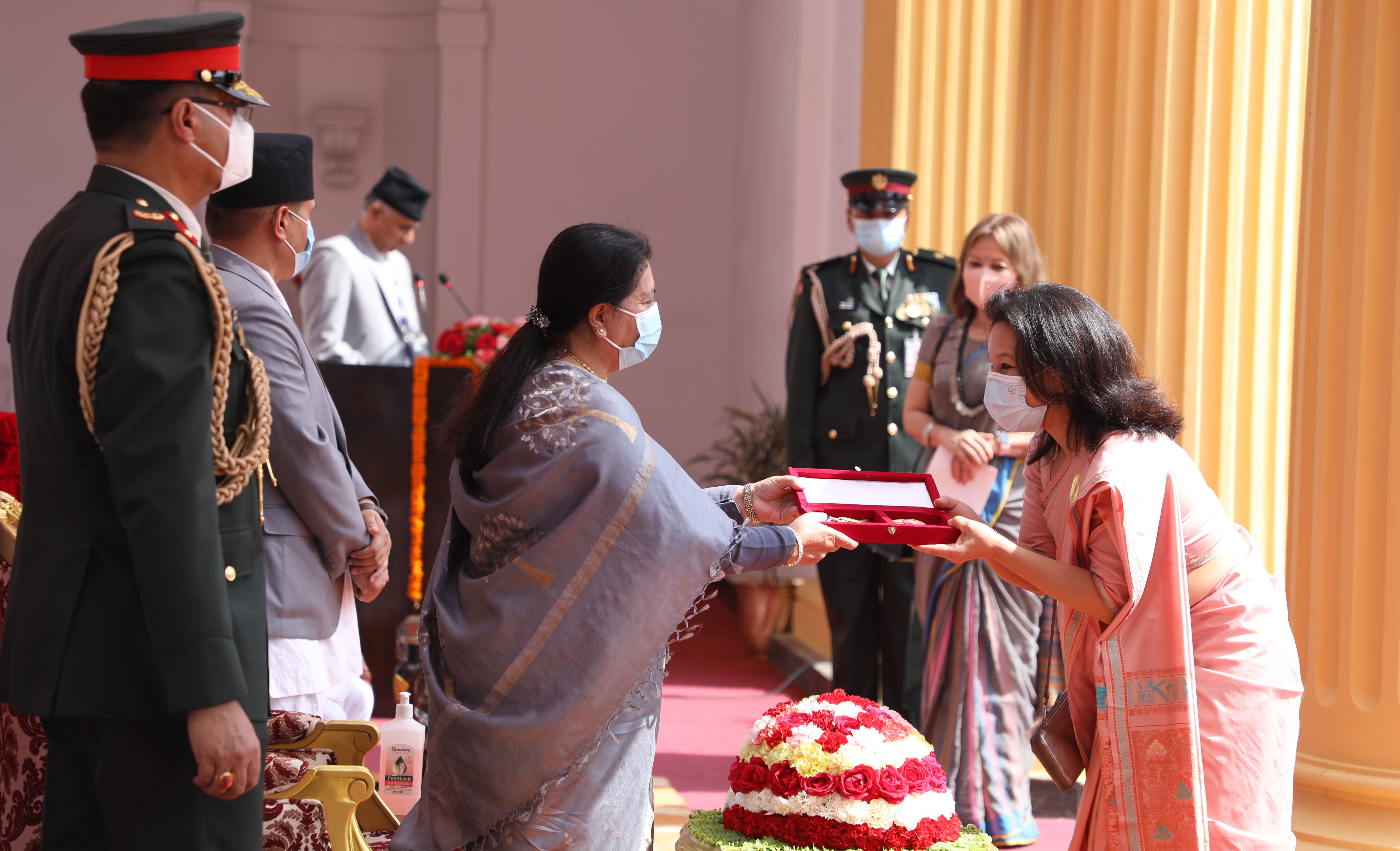
President Bhandari confers decorations (Photo Feature)
14 Apr, 2022