Climate Conservation Key To Ecotourism
Babul Khanal
Environmental conservation and sustainable development (ECSD) constitutes important component of development discourses in the modern day world. The ECSD has found space in the national and international forums as it is invariably interlinked to climate change triggered by the global warming, increase in the sea level, snow melting and land erosion. The climate change has badly hit the poor and vulnerable people as their livelihoods are being gradually destroyed owing to this phenomenon. Threat of population pressure and poverty has massively damaged rainforests, wildlife areas, habitats and biological resources in many countries, including Nepal.
Natural resources
Natural resources form the basis of the development of Nepal. Especially, the tourism industry based on the natural resources is evolving as an important avenue for local economic development in form of employment generation and foreign currency earning. The natural and cultural environment is the key to eco-tourism. National parks, climate smart villages (CSV), community gene/seed banks and botanical gardens attract a huge number of tourists, contributing to the conservation of the natural habitats as well as creation of local jobs.
The issue of climate change has received greater limelight today but the need for establishing the protected areas for the purpose of environmental and ecological conservation was felt long ago. Considering the recreational needs of the people, the national parks are being promoted as part of eco-tourism in Nepal. As a World Heritage Site and home of indigenous people such as Tharus and Botes, Chitawan National Park includes the Ramsar site, Beeshajari Lake, and buffer zones. The vicinity of the park contains vital sources of livelihoods for such indigenous people. They earn their livelihoods from agriculture, forests, livestock, fisheries, tourism, non-timber forest products, hunting and gathering. Eco-tourism activities have benefitted the people, enabling them to generate self-employment, boost the community development and reduce conflict between the park and the locals.
Climate change has affected agricultural productivity causing food insecurity and migration. Several agencies had started the initiatives to lessen the effects of climate change on agriculture were started. Climate Smart Village (CSV) is such a scheme implemented with the purpose of building affordable and replicable adaption pilots in mountain areas based on the climate adaption, resilience and food security approach to support the communities. The CSV carries various elements including crop, ICT, energy, nutrient and security. Maintenance of the soil fertility and moisture is carried out through crop rotation, mixed cropping, intercropping with the use of biogas, bio-fertilizer and bio pesticides. For this, farmers are informed via different means of communication, trainings and security schemes.
Due to the increased human pressure and climatic impacts, there is the loss of biodiversity, agricultural land, and genetic resources. As an attempt of securing indigenous seed, it is stored in a moisture-controlled temperature. National Gene Bank coordinates to conserve the varieties of the gene from the community seed banks (CSBs), farmers’ cooperatives, scientists, etc. The importance of CSBs lies in the collection, distribution, regeneration, and multiplication of the seeds besides strengthening the farmers in their on-farm conservation activities to cope with climate change. Community ownership and viability is the strong aspects of such approach.
National Botanical Garden (NBG) situated in Godavari, Lalitpur was established as a site for testing the integrated mountain development and the sustainable farming practices. It has preserved hundreds of species of plants, trees, shrubs, climbers, exotic trees and endangered plants having medicinal values. The place attracts many domestic tourists throughout the year as it is famous for the picnic spot. The NBG deserves a great value since it provides housing and care for specimens of endangered species and breed of plants. Besides, the herbariums inside the garden have the significance in preserving the endangered species.
Approaches
Initiatives for environmental conservation have contributed to protecting the ecosystem including the biological resources. Different approaches have been applied for the conservation of biological resources through the promotion of protected areas, gene/seed banks, organic agriculture, etc. It has contributed to make between the nature and human beings. These efforts have great value for local economic development through eco-tourism and employment generation with community participation.
The cultural promotion, awareness, education, & health safety issues should be addressed to conserve the wildlife, environment and indigenous culture for the long term sustainable development. Nepal is endowed with the rich biodiversity that enhances the greater prospect of ecotourism. Enabling policies and laws need to be framed to boost the ecotourism that contributes to overall development of tourism sector as well preservation of climate that is constantly under threat owing to the global warming.
(Khanal is the deputy general manager of National Cooperative Federation of Nepal)
Recent News

Do not make expressions casting dout on election: EC
14 Apr, 2022
CM Bhatta says may New Year 2079 BS inspire positive thinking
14 Apr, 2022
Three new cases, 44 recoveries in 24 hours
14 Apr, 2022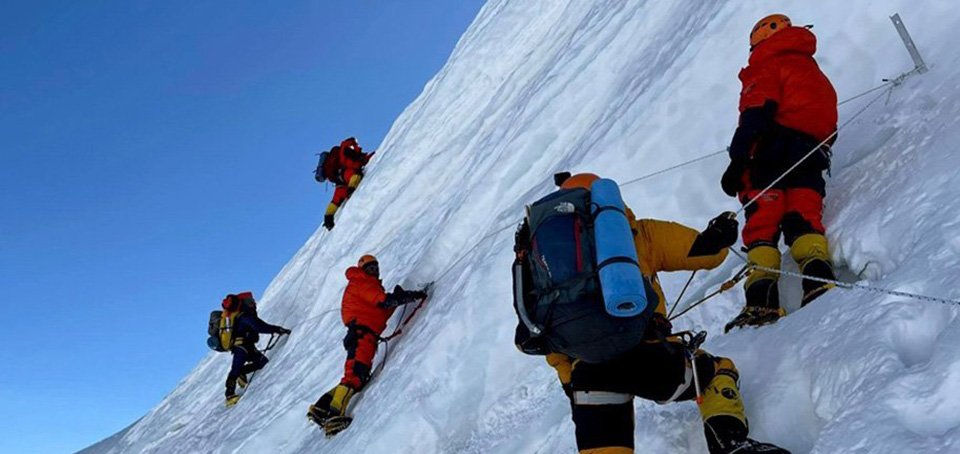
689 climbers of 84 teams so far acquire permits for climbing various peaks this spring season
14 Apr, 2022
How the rising cost of living crisis is impacting Nepal
14 Apr, 2022
US military confirms an interstellar meteor collided with Earth
14 Apr, 2022
Valneva Covid vaccine approved for use in UK
14 Apr, 2022
Chair Prachanda highlights need of unity among Maoist, Communist forces
14 Apr, 2022
Ranbir Kapoor and Alia Bhatt: Bollywood toasts star couple on wedding
14 Apr, 2022
President Bhandari confers decorations (Photo Feature)
14 Apr, 2022